Abstract
The current study discusses the metafunctional diversity of nominalized thematic structures in Achebe’s (1958) English novel, Things Fall Apart and in its Urdu translation, Bikharti Duniya (Ullah, 1991). For statistical measurement, O'Donnell’s (2008) scheme of the UAM Corpus tool has been used to annotate the selected corpus. After annotation, some nominalized themes in English and Urdu have been screened to interpret their grammatical realization, functional significance, thematic progression (McCabe, 1999) and unmotivated displacements of nominalized themes. The results show that the grammatical realization of nominalized themes in English and Urdu varies due to the verbs marked with gender and numbers. Additionally, the English and the Urdu nominalized themes go parallel in theme markedness but the difference is observed when the thematic information units become rhematic information units.
Key Words
Nominalization, Theme, Rheme, Corpus, English, Urdu
Introduction
This research focuses on the textual metafunction and its lexico-grammatical parameters to figure out the nominalized thematic structures with thematic progression. Thematic structures, with the help of their line of meanings, organize the message of a clause. The thematic structure of a clause consists of two distinct parts i.e. theme and rheme, which constitute the message. To constitute the message, the position of the theme is indicated as clause initial. The element of theme decides the upcoming message. It is chosen by the speaker as a point of departure in order to make the hearer interpret the information confined in the message. The element of rheme accompanied by theme is termed as remainder which completes the structure and information of the clause. In this way, the present work intends to investigate the theme-rheme sequence in the thematic structures of English and Urdu clauses by determining the aspects of nominalization. In this study, the thematic progression of the nominalized themes in English and Urdu has also been investigated to determine a particular flow of information.
Many kinds of research including contrastive analysis of languages, have been conducted by applying the theory of SFL. The metafunctions of English in comparison with other languages have been investigated in a number of studies on translation (Steiner, 2002; Kunz et al., 2014). The lack of investigation regarding textual metafunction in English and Urdu causes a research gap, so in order to fill this research gap, the existing study encompasses the parameters of textual metafunction and especially the nominalized themes in English and Urdu.
This research aims to identify the English and Urdu nominalized themes according to the parameters proposed by Halliday (1985). It also aims to check out the difference in frequency of nominalized thematic structures by tagging English and Urdu corpus. The major aim of this study is to locate the grammatical realizations, functional significance and thematic progression of the nominalized themes. Based on the objectives, this study is carried out with three research questions.
1- What is the grammatical realization of the nominalized themes in English and Urdu?
2- What are the functional significance and thematic progression of nominalized themes in English and Urdu?
3- How effectively have the nominalized themes in English been translated into Urdu?
This study will help the writers compose literary texts according to their contextual specifications. The current study will raise awareness of ESL and EFL teachers, instructional designers and researchers to provide learners and writers with effective academic writing instructions regarding the use of nominalized thematic structures.
Literature Review
Nominalization
Nominalization is termed a
grammatical metaphor (Halliday & Martin, 1993). A kind of density is found in nominalization-oriented
texts and discourses because the information is compacted and it becomes hard
to process due to nominalization. Nominalization performs certain functions.
Firstly, the verb is likely to be converted into a noun. In the other function,
subject or object positions in an equative sentence are occupied by
nominalization restricting the process of source verbs.
Nominalization is also discussed as part of
lexicogrammatical realizations. Nominalization is reflected by a thematic
structure having two or more separate elements. The elements are liable to form
a constituent as a theme. This kind of theme is called a nominalized theme due
to the combination of a nominal group and its complement. The combination of
the nominal group and its complement is determined by relative pronouns: what,
who, that, whose and whom. The clause containing nominalized theme
is interpreted as ‘thematic equative’ (Halliday,
1967) because
of theme and rheme share equality in this clause. Such a clause is known as
identifying clause. Thematic equative permits theme and rheme structures to set
up an equation. In nominalization, thematic equative structures possess equal
identity, so theme and rheme can be placed in reverse order. Furthermore, two
semantic features as two senses of the word identity are realized by thematic
equative (Halliday, 1985). A thematic source grouping two or more
constituents of the theme and rheme structure are called thematic equative. The
following table describes the thematic equative.
Table 1. Thematic Equative as Theme and Rheme
|
Nominalization as Theme |
||
|
What no one seemed
to notice |
was |
The writing on the wall |
|
Theme |
Rheme |
|
|
Nominalization as Rheme |
||
|
Twopence a day |
was |
what my master allowed me |
|
Theme |
Rheme |
|
In thematic equative, two constituents are
linked by a relationship of identity that is expressed by a form of the verb be.
The nominalized structure is a nominal group comprising a head and a post
modifying relative clause. The head and post limiting relative clauses are
joined by relative pronouns: what, that, who, whose and whom etc.
In fact, thematic equative permits the head and its relative clause to design
nominalized thematic structures. Moreover, thematic equatives are of two types:
unmarked thematic equative and marked thematic equative. An unmarked thematic
equative allows nominalization in the theme and the nominalized theme functions
as the subject of the clause. The marked thematic equative also allows
nominalization in theme but such sort of nominalized theme functions as an
adjunct of the clause. Both types of thematic equatives have semantic features
of exclusiveness through which unmarked and marked nominalized themes extend
their meanings to establish their combination with rheme. The subsequent table
displays the projection of unmarked and marked nominalized themes in italics.
Table 2. Marked and Unmarked Nominalized Themes
|
Theme |
Function |
Class |
Example |
|
Unmarked |
Subject |
Nominalized clause as head |
What I desire is a good pair of shoes. |
|
Marked |
Adjunct, Complement |
Nominalized clause as head |
What I desire, I will purchase soon. |
Moreover, nominalization in thematic equative
can be considered either as a theme or as a rheme. The present study has been
carried out by focusing on the aspect of thematic equatives in nominalization.
Previous Studies
There are studies including
contrastive analysis of the metafunctions of different languages. As Rose (2001) analyzed languages including Chinese, French,
Gaelic, German, Japanese, Pitjantjatjara, Tagalog and Vietnamese to investigate
variations in their themes. He selected akin corpus from the profiles of the
grammars of these languages (Caffarel et al., 2004). Textual resources of the languages were
focused on for the research. The researcher concluded that the languages
contain diverse textual organizations due to variations in social contexts. The
thematic structures of Spanish and English were investigated by McCabe (1999). In addition, for the thematic analysis in
translation, a study applying theme-rheme sequence to the translation between
Korean and English was conducted by Kim (2007). Her study hypothesized that there was still a
gap between translation studies and SFL, especially in the application of
thematic analysis. She analyzed the translation between English and Korean,
focusing on two things: (1) major difficulties in the application of SFL-based
theme analysis and (1) the ways in which they had been addressed (Kim, 2007a, 2011a, 2011b). Her study concluded with some
suggestions for the combined research regarding SFL and translation studies.
Another contrastive study was conducted by
Lavid et al. (2010) to contrast the grammar of Spanish and English. The
findings revealed that Spanish nominal groups diverge from their English
counterparts in three main areas: (1) the realization of the Thing as a
pronoun, (2) the functional distribution of Deictics, and (3) the logical
structure of the constituents. Furthermore, the grammatical properties of
thematic equatives and nominalization in terms of their themes in news reports
and editorials have also been investigated (Francis,
1990). With
reference to these studies, the current study involves the analysis of
nominalized thematic structures and their thematic progression, for which the
methodology has been defined in the following section.
Research Methodology
To accomplish this piece of research, the mixed
methods approach has been used. Firstly, the quantitative analysis determines
the differences in frequency in the English and the Urdu texts, and secondly,
the qualitative analysis describes all the differences in greater detail. The
parameters of systemic functional linguistics (Halliday,
1994) and the
patterns of thematic progression (McCabe, 1999) have been applied as a theoretical framework.
Samples
The samples of the present
study were selected from electronic sources by defining purposive sampling
criteria. Achebe’s (1958) novel, Things Fall Apart and its Urdu
translation, Bikharti Duniya (Ullah, 1991), were selected to compile English and Urdu corpus.
Corpus
Size
Due to semi-automatic annotation, the size of
the corpus was small. The two texts, including almost 50,000 words each, have
limited the size of the corpus. The two corpora containing almost 100,000 words
were open-ended because the new annotation schemes were incorporated into
existing ones at different points.
Annotation
of the Corpus
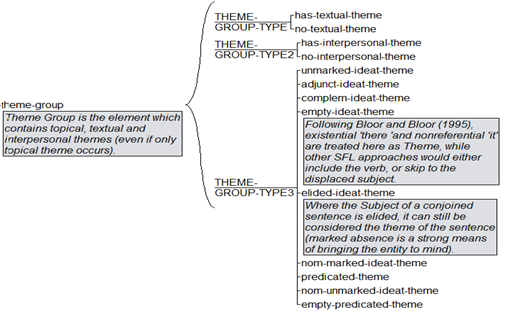
The annotation of the data in English and Urdu Corpus (EUC) was done by UAM Corpus Tool (O’Donnell, 2008) semi-automatically and manually. The UAMCT allows the researchers to make additions and to design their own schemes applying the tags either in a similar way or a different way. This corpus tool was selected due to the unavailability of a fully automatic tool to identify SFG features, especially in the Urdu corpus. The developed corpus was processed in the UAM corpus tool for the annotation regarding nominalized thematic structures. The following annotation scheme was imported from UAMCT for annotation purposes.
Figure 1
The scheme of the UAM Corpus Tool
Data Analysis and Procedure
The annotated English and Urdu corpus were used to collect the data. The classification of nominalized themes presented by Halliday (1994) was incorporated. For Urdu grammatical structure, the descriptions given by Schmidt (1999) were incorporated. Some clauses were chosen to analyze the functional significance and thematic progression for which the sequence of theme-as-given and rheme-as-new or vice versa was adopted. The figures were designed to show the flow of information units. The translation of some Urdu clauses in comparison with English clauses was investigated and the frequency of the English and the Urdu nominalized themes were mentioned in the tables.
Results and Discussion
Grammatical Realization of Nominalized Themes
in English and Urdu
Generally, in English, a nominalized thematic
structure consists of a noun or a nominal phrase followed by a modifying
relative clause and further, it is a thematic equative that promotes the sense
of exclusiveness and identification. Likewise, in Urdu, a nominalized thematic
structure is also a thematic equative promoting the sense of exclusiveness and
identification but its syntactic structure is different because of grammatical
gender and free-word order (Butt & King, 2007) in Urdu. In Urdu, the nominalized theme
markedness also follows the parameters presented by Halliday
(1994). To
carry the discussion forward, the following nominalized thematic structures
from English and Urdu corpus have been screened. Consider the first example to
show the difference in theme markedness.
a. ? mæn hu? k?m?ts ?t w?l n?t bi b?r?d ba? h?z klænzm?n.
b. x?d?k??i k?rne v?le ki t??d?fin me? ?ske q?bile v?le ??s? n?hi let?e.
The English clause in (1a) has an unmarked nominalized theme
including a nominalization marker who and a finite verb, whereas the
Urdu clause in (1b) has an adjunct as a marked nominalized theme including
covert nominalization and a non-finite verb. The marked nominalized themes
including covert nominalization and non-finite verbs, are also created in
English. As the unmarked nominalized theme, a man who commits it can be
converted into the marked nominalized theme e.g. a man committing suicide
in which the nominalization marker seems covert but the noun performing an
action is always visible. But the marked nominalized theme x?d?k??i k?rne v?le ki t??d?fin me? (*in
the burial of committing suicide) does not contain a visible noun performing an
action but this theme contains a clitic or an oblique-infinitive maker v?l? which is known as the agent of an action (Schmidt, 1999). This clitic is used with the verbal nouns (non-finite verbs) in
Urdu because it is marked with gender and number. Due to the presence of this
clitic, the nouns and nominal phrases can be omitted from the marked
nominalized themes in Urdu because of the various forms of this clitic e.g. v?l? (Singular + Masculine), v?le (Singular/Plural + Masculine), v?li (Singular + Feminine), v?lij?? (Plural + Feminine) seem
nominal markers as well. So, it is evident that the clitics or
oblique-infinitive markers also contribute to the theme markedness of
nominalized themes in Urdu. This formation is not common in English. The
forthcoming examples discuss the correlative construction in the Urdu
nominalized themes.
a. ð? ???z evri mæn l??nd w?z ð? læ??w?d? ?v ð? h?l??d a?t w?dn? ?nstr?m?nt.
b. vo ?iz? ?o q?bile k? h?r ??xs sikht?? t?h? ?n me? se ek l?k?i ke ?s ?le ki z?b?n s?m??hn? t?h?.
These clauses differentiate
correlative construction between English and Urdu nominalized themes. In
English, correlatives are used as coordinating and subordinating conjunctions.
The English nominalized themes do not include specific correlatives but some
similar constructions seem possible. On the contrary, Urdu accommodates a
unique correlative construction vo-?o (that-which) opposite to the correlative conjunction ?o-vo (which-that) (Butt &
King, 2007; Schmidt, 1999). This correlative construction is usually
used to create embedded and extraposed clauses in Urdu. The Urdu nominalized
theme (embedded clause) in (2b) begins with the demonstrative vo which
correlates with the relative ?o and an NP-modifying clause. The English nominalized theme in (2a)
shows an unmarked thematic prominence without incorporating any demonstrative
at the clause-initial position. The next clauses exhibit the usage of
nominalization markers in English and Urdu nominalized themes.
a. ?nd p?hæps ð??z n?t s?? j?? w?d bi ple??? ?n pe?z
?n les ??p?n ple?s?z.
b. ??r ??l?b?n vo b??e ?o ?b ?t?ne ?hote n?hi r?he t?he ?o?? ?o?? b?n k?r ?n ??ghõ m? ?o k?m kh?li hot??? khelt?e.
These clauses illustrate that
the nominalization marker following a noun or a nominal phrase can be used both
overtly and covertly in English. As the English nominalized thematic structure
in (3a) starts with a nominal phrase modified by a covert nominalization marker
and an NP-modifying clause. In this structure, not only nominalization marker who
but also finite verb seemed covert but the sense of thematic nominalization can
be observed clearly. And due to thematic nominalization, the equation of this
structure is also possible e.g. In less open places, there would be playing
those who were not so young. The same is not true for the Urdu nominalized
theme because the nominalization markers and finite verbs are always used
overtly. As the Urdu nominalized thematic structure in (3b) includes a visible
nominalization marker ?o (who) and a finite verb t?he (were). In this way, nominalized structures are created
differently in English and Urdu.
Functional Significance of
Nominalized Themes
The nominalized thematic structures of English
and Urdu resemble each other with regard to their functional significance; and
flow of information. Generally, a thematic structure generates a message
occupying a theme as clause-initial elements which obtain given information and
a rheme as the remaining elements which involve new information but on the
contrary, the opposite information sequence is also possible (Halliday, 1994). The same is true for the nominalized themes in
English and Urdu as well. Although the clauses of thematic nominalization are
constructed in multiple ways, they go parallel in creating coherence in any
message. The significance of thematic nominalization in English and Urdu is
twofold: (1) it makes the theme an exclusive element or an identifying theme
and (2) it makes the whole clause an equation in which the theme and the rheme
can interchange their position and information. The interchange of theme and
rheme causes to shift nominalization in the rheme. The following discussion
figures out the thematic progression patterns.
Table 3. Thematic
Progression of Nominalized Themes in English
|
Thematic
Structures |
Thematic Progression |
Peripheral Theme |
|||
|
Linear Theme |
Constant Theme |
Split Theme |
Split Rheme |
||
|
Unmarked Nominalized Theme |
8% |
32% |
0% |
0% |
74% |
|
Marked Nominalized Theme |
2% |
3% |
0% |
0% |
10% |
|
Overall Frequency |
10% |
35% |
0% |
0% |
84% |
The table shows that in nominalized thematic
structures, the unmarked themes bear 32% while the marked themes carry only 3%
constant thematic progression. This difference in frequency manifests that firstly,
unmarked nominalized thematic structures are more frequent than marked
nominalized thematic structures in English text and secondly, unmarked
nominalized themes link the flow of information with their preceding themes
more constantly than marked nominalized themes in English. The maximum 74% of
unmarked nominalized themes and the minimum 10% of marked nominalized themes
are placed as peripheral themes which do not share the flow of information with
their preceding themes and carry new information necessarily. In the end, it is
obvious that the English nominalized themes, both unmarked and marked, are
observed at the peripheral position with 84% frequency which is more than the
frequency of 35% of constant themes and the frequency of 10% of linear themes.
Table 4. Thematic
Progression of Nominalized Themes in Urdu
|
Thematic
Structures |
Thematic Progression |
Peripheral Theme |
|||
|
Linear Theme |
Constant Theme |
Split Theme |
Split Rheme |
||
|
Unmarked Nominalized Theme |
6% |
10% |
0% |
0% |
43% |
|
Marked Nominalized Theme |
5% |
13% |
0% |
0% |
32% |
|
Overall Frequency |
11% |
23% |
0% |
0% |
75% |
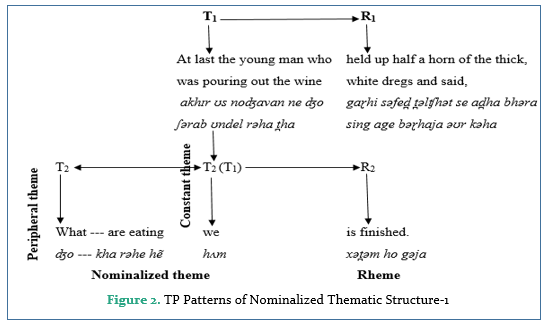
Figure 2
TP Patterns of Nominalized Thematic Structure-1
These clauses point out the function of thematic nominalization in English and Urdu. The English clauses (4) and the Urdu clauses (5) secure thematic nominalization because of the placement of an embedded clause into the matrix clause which ultimately turns out to be a thematic equative. Actually, the message has been encoded with thematic nominalization to make the information exclusive which means this and this only and nothing else. The encoder creates the structures of thematic nominalization to identify and specify particular thematic information which equates with rhematic information. The nominalized thematic information units have an interpersonal association and are unmarked in both English and Urdu clauses because they are placed as subjects. Additionally, the flow of information is examined by applying the patterns of thematic progression. The nominalized themes seem to carry give and new information. Due to the presence of interpersonal pronominal marker, the information has been projected by constant thematic progression in the nominalized theme. Besides, due to the presence of the rest of the elements, the new information is also projected by a peripheral theme. The rhemes of both English and Urdu clauses carry new information. In this figure, the T1 is repeated as a constant theme in T2 but T2 also has new information at the periphery. The R1 does not share its information with the following theme and rheme. The next thematic structures show different theme markedness and information flow as compared to the previous thematic structures. The nominalized theme is located at the periphery but the pronominal element of the nominalized theme links its information with the preceding theme bearing constant thematic progression. Here, the thematic progression sequence is considered to be twofold. The subsequent nominalized thematic structures furnish a different way of thematic progression patterns. The following figure shows a different thematic progression of the nominalized thematic structures.
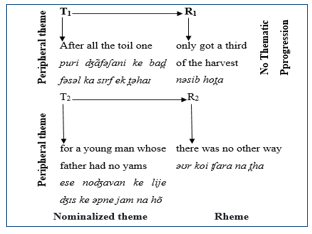
Figure 3
TP Pattern of Nominalized Thematic Structure-2
These thematic structures confirm the placement
of nominalized themes after textual themes in English and Urdu. The nominalized
theme in the English clause is a marked theme because it is placed as an
adjunct associated with its matrix clause as the rheme. Despite being an
adjunct, the sense of thematic nominalization makes the whole clause a thematic
equative. And in this thematic equative, the exclusive information is about
only that young man whose father had no yams. The same is observed in the Urdu
clause. The flow of information is also parallel to the nominalized thematic
structures of English and Urdu. The nominalized theme seems to be placed at the
periphery because it contains new information. This nominalized theme does not
share its information with any of the preceding themes and rhemes. Taking into
account these examples, it is evident that the functional significance
particular to the thematic progression of nominalized thematic structures is
identical in English and Urdu. The next segment confers the analysis of
nominalized thematic structures in English and Urdu.
Problems
in Translation of English Nominalized Themes into Urdu
In this section, the analysis of English and
Urdu nominalized thematic structures: ideational, interpersonal, and textual
has been presented. In ideational thematic structures, the themes of
declarative clauses are nominalized. In interpersonal thematic structures, the
themes of declarative, interrogative, exclamatory and optative clauses are
nominalized. And in textual thematic structures, themes of all types of clauses
are nominalized after conjunction, conjunctive adjuncts and continuatives.
Moreover, nominalized thematic structures are categorized as unmarked
nominalized themes and marked nominalized themes. The former are used as
subjects of a clause whereas the latter are considered to be objects of a clause.
Following this sequence, the annotation of English and Urdu nominalized
thematic structures have been analyzed and their frequency of occurrence is
counted in the succeeding table.
Table 5. Nominalized
Themes and Nominal Markers in English and Urdu
|
Thematic
Structures |
English Nominalization Markers |
Urdu Nominalization Markers |
||
|
Unmarked Nominalized Themes |
Who |
66% |
?o / ??s / ??n / ??nh? |
18% |
|
What |
8% |
?o / ?o k??h |
1% |
|
|
Whose |
7% |
??s k? / ??s ke / ??s ki |
6% |
|
|
When |
1% |
??b |
17% |
|
|
Where |
1% |
??h?? |
11% |
|
|
Whom |
4% |
??s ko / ??n ko |
1% |
|
|
That |
15% |
?o / ??s / ??n |
10% |
|
|
Which |
12% |
|||
|
Marked Nominalized Themes
|
Who |
2% |
?o / ??s / ??n |
12% |
|
What |
1% |
?o / ?o k??h |
12% |
|
|
Whose |
1% |
??s k? / ??s ke / ??s ki |
3% |
|
|
When |
3% |
??b |
4% |
|
|
Where |
0% |
??h?? |
3% |
|
|
Whom |
0% |
??s ko / ??nh? |
1% |
|
|
That |
1% |
?o / ??s / ??n |
13% |
|
|
Which |
3% |
|||
Observing nominalized themes, the difference in
frequency figures out that nominalized unmarked themes are more frequent in
English than in Urdu, while nominalized marked themes are frequent in Urdu. The
frequency of the very first nominalization marker is 66%, while its Urdu
equivalents appear with the lowest frequency of 13%. This difference is due to
two reasons. Firstly, the English nominalization marker appears in only
unmarked thematic structures, while its Urdu equivalents appear not only in
unmarked but also in marked thematic structures. Secondly, during translation,
most of the nominalized themes in English have been shifted into the rhemes in
Urdu. This is also true to the next nominalization marker that occurs with the
8% frequency in unmarked English themes. On the other hand, its equivalents ?o and ?o k??h appear with 12% frequency in Urdu marked themes. The frequency of
the nominalization marker when is less in English unmarked and marked
themes than the frequency of its equivalent ??b in Urdu unmarked and marked themes because the marker when
is mostly used as subordinating conjunction in English while the maker ??b seems to be a nominalization marker which creates a complement
clause for the preceding nouns in Urdu. Furthermore, in Urdu, not only when
but also as has been translated as ??b in the initial clause of nominalization so, the Urdu contains a
higher frequency of nominalized themes than English. The next nominalization
marker where is also used as subordinating conjunctions in English,
mostly so; it is less frequent in English. The marker ??h?? also creates a complement clause for its preceding nouns and in
this way, it appears with 11% and 3% frequency in Urdu unmarked and marked
themes, respectively. The next nominalization marker is more frequent in
English because many English nominalized themes have been translated as Urdu
rhemes. The same is true for the next nominalization markers which and that
which appear with 12% and 15% frequency. On the other hand, their three
Urdu equivalents, ?o, ??s and ??n, occur with the lowest frequency of 10% due to the appearance of
mostly nominalization markers in rhemes. Another reason is that many unmarked
nominalized themes in English have been translated as marked nominalized themes
in Urdu. In this reference, the frequency of 13% of Urdu nominalization markers
?o, ??s and ??n in marked thematic structures becomes a proof.
In the next section, only finite nominalized
thematic structures have been selected from the English and Urdu corpus. Some
other clauses preceding nominalized thematic structures have also been taken to
check the flow of information among them. The whole analysis reveals that
English nominalized themes have been translated as simple prepositional
phrases, nouns and nominal phrases etc. In this way, the translated Urdu themes
lose the sense of nominalization and become topically unmarked and marked
themes. During translation, unmarked nominalized themes in English have been
placed as rhemes in Urdu and vice versa. Due to unmotivated displacement of
themes, translation choices seem ambiguous and convey misleading information as
the following clauses indicate the conversion of an unmarked nominalized theme
into a simple topical theme.
Table 6. Conversion of Unmarked Nominalized Theme into
Topical Theme
|
English
Source Text |
||||
|
CL |
Theme |
Rheme |
||
|
Nominalized/Topical |
||||
|
1.1a |
Okonkwo |
w?z s?t?? ?n ? ???tsk?n ??lredi
i:t?? h?z f?:st wa?fs mi?l. |
||
|
1.2a |
Obiageli, hu? h?d br??t ?t fr?m h? m?ð?z h?t, |
sæt ?n ð? fl?: we?t?? f?r h?m tu f?n??. |
||
|
Urdu Target Text |
||||
|
CL |
Theme |
Rheme |
||
|
Textual |
Adjunct |
Topical |
||
|
1.1b |
|
|
Okonkwo |
b?kri ki kh?l p?r beth? b??i bivi ke gh?r se ?j? kh?n? kh? r?h? t?h?. |
|
1.2b |
|
|
Obiageli |
?pni m?? ki ?honp??i se kh?n? l?i t?hi |
|
1.3b |
??r |
?b |
--- |
f?r? p?r bet?hi ?ske x?t??m k?rne k? ?nt?ez?r k?r r?hi t?hi. |
The analysis describes that the first clause in
(1.1a) begins with a subject as unmarked topical theme carrying given
information which is associated with the rheme carrying new information. The
translated clause in (1.1b) shows a similar division of theme and rheme as in
(1.1a). But the next nominalized clause in (1.2a) is not translated as a
nominalized clause in (1.2b). The nominalized theme Obiageli, hu? h?d br??t ?t fr?m h? m?ð?z h?t, is placed at the periphery carrying new information and it also
carries given information due to sharing linear information flow with the
preceding rheme. On the other hand, its translated theme is an unmarked topical theme Obiageli placed
at the periphery bearing only new information because the given information ?pni m?? ki ?honp??i se kh?n? l?i t?hi
(brought food from her mother’s hut) has been shifted into the rheme in (1.2b).
Additionally, the sense of nominalization and identification is not found in
this translated theme. The omission of nominalization removes the possibility
of thematic equative and causes ambiguity in conveying exact meaning. As the
English nominalized theme identifies and specifies that Okonkwo was eating that
food that only Obiageli brought from her mother’s hut. But its translated
topical theme is a declarative statement which means that Okonkwo was eating
some other food while Obiageli brought different food from her mother’s hut. In
Urdu translation, another ambiguity occurs due to making the rheme of English
nominalized clause as the third clause in (1.3b). This extended clause has been
joined to the preceding clause in (1.2b) by paratactic conjunction and a
conjunctive adjunct. Here, along with the ambiguous meaning, the flow of
information is also misleading. To avoid this ambiguity, another translation
choice e.g. Obiageli ?o ?pni m?? ki ?honp??i se vo
kh?n? l?i t?hi, f?r? p?r bet?hi ?ske x?t??m k?rne k? ?nt?ez?r k?r r?hi t?hi can be
considered. The next
analysis interprets the English marked nominalized theme into Urdu topical
theme.
Table 7. Conversion
of Marked Nominalized Theme into Topical Theme
|
English Source Text |
||||
|
CL |
Theme |
Rheme |
||
|
Nominalized/Topical |
Displaced |
|||
|
2.1a |
s?t? ?ten?n? |
|
w?d ??v ð? ne?t?vz ? p?? ?p?n??n ?v h?m. |
|
|
2.2a |
?n ð? b?k w?t? hi:
plænd tu ra?t |
hi: |
w?d stres ðæt p??nt. |
|
|
Urdu Target Text |
||||
|
CL |
Theme |
Rheme |
||
|
Adjunct |
Topical |
Displaced |
||
|
2.1b |
ese moq? p?r mo?ud?gi se |
|
muq?mi log |
?ske b?re me? gh?tij? r?e q?em k?r s?kt?e he?. |
|
2.2b |
|
vo |
|
?pni zere t???viz kit??b me? ?s n?kt?e p?r x?susi zor d?eg?. |
The English topical theme carrying given
information in (2.1a) is translated as an adjunct in the Urdu clause (2.1b).
The rheme carrying new information in clause (2.1a) is translated as the
displaced theme in (2.1b). Some of the new information in rheme continues to be
selected in the following nominalized theme in (2.2a). Despite this linear flow
of information, a marked nominalized theme is placed as a peripheral theme
carrying new information. And being an adjunct, the marked nominalized theme
displaces the topical theme also carrying given information. Moreover, in the
Urdu translation, the English marked nominalized theme has been divided into
the topical theme and the rheme in (2.2b). The topical theme has no
nominalization sense and shares a linear flow of information from its preceding
rheme while the rheme has new information in (2.2b). These translation choices
create not only ambiguity in conveying appropriate meaning but also problems in
delivering exact information. As the English nominalized theme delivers the
information that he has planned to write a book, whereas the translated topical
theme means a person only. Here, to create a nominalized theme in Urdu, a
suitable translation e.g. ?s kit??b me? ??se l?khne k? ?sne so?? t?h? vo ?s n?kt?e p?r x?susi zor d?eg? can be considered. The subsequent clauses explain
the nominalized theme in English as an adjunct to Urdu.
Table 8. Conversion
of Unmarked Nominalized Theme into Adjunct Theme
|
English
Source Text |
||||||
|
CL |
Theme |
Rheme |
||||
|
Textual |
Nominalized/Topical |
|||||
|
3.1a |
wen |
hi: |
f?n??t h?z k??l? n?t |
|||
|
3.2a |
|
hi: |
sed |
|||
|
3.3a |
|
“ð? ???z ðæt hæp?n ði?z de?z |
a: veri
stre?nd?”. |
|||
|
Urdu Target Text |
||||||
|
CL |
Theme |
Rheme |
||||
|
Textual |
Adjunct |
Topical |
Displaced |
|||
|
3.1b |
??b |
|
Vo |
|
kola nut k? tuk?? x?t??m k?r ??k? |
|
|
3.2b |
t?o |
|
?sne |
|
k?h?, |
|
|
3.3b |
|
“?? k?l |
|
??ib v?qej?t? |
run?m? ho r?he he?”. |
|
These clauses demonstrate the conversion of the
English unmarked nominalized theme into Urdu adjunct theme. The English clause
in (3.1a) includes hypotactic conjunction as the unmarked textual theme and an
unmarked ideational/topical theme carrying given information which continues to
be selected in the unmarked ideational/topical theme of the clause (3.2a). The
rhemes of both clauses convey new information. The translated Urdu clauses in
(3.1b) and (3.2b) have similar thematic structures and flow of information as
in the English clauses (3.1a) and (3.2a). But the nominalized theme of the
things that happen these days in the English clause (3.3a) has been
translated as the adjunct ?? k?l (these days), the displaced theme ??ib v?qej?t? (strange things) and the rheme run?m? ho r?he he? (are happening) in the Urdu clause (3.3b).
Here, these English and Urdu themes share the interpersonal context. The
English nominalized theme is placed at the periphery having new information.
The Urdu adjunct theme and displaced theme are also arranged at the periphery
carrying new information but they do not convey any exclusive information in
the form of thematic equative. As the English nominalized theme gives a piece
of exclusive information that the strange things are only those that happen
these days. In other words, no strange happening was observed in the past. On
the contrary, the translated adjunct and displaced themes give the impression
that these days, strange things are happening and they might have happened in
the previous days as well. This ambiguity has occurred due to the absence of
nominalization. To secure the thematic nominalization and exclusive information
in the Urdu clause (3.3b), the suitable translation choice possible e.g. vo
v?qej?t? ?o ?? k?l run?m? hot?e he? boh?t? ??ib he?. The following clauses declare
that the English nominalized thematic structure has been converted into the
Urdu clauses of correlative conjunction.
Table 9. Conversion
of Unmarked Nominalized Theme into Correlative Conjunction
|
English Source Text |
|||
|
CL |
Theme |
Rheme |
|
|
Nominalized/Topical |
|||
|
4.1a |
s?t? st??r?z |
w? spred ?n ð? w?:ld ba? ð? dev?l tu li:d m?n ?stre?. |
|
|
4.2a |
ð??z hu? b?li?vd s?t? st??r?z |
w? ?nw??ði ?v ð? l??dz te?bl?. |
|
|
Urdu Target Text |
|||
|
CL |
Theme |
Rheme |
|
|
Textual |
Topical |
||
|
4.1b |
|
esi k?h?nij?? |
?et?n d??nij? me? logo? ko g?mr?h k?rne ke lije ph?l?t?? he. |
|
4.2b |
?o |
log |
?n k?h?nijõ p?r j?kin r?kht?e he? |
|
4.3b |
vo |
--- |
?q? ki mæz ke g?rd?
bethne ke eh?l n?hi. |
This analysis reveals a significant difference in the Urdu translation of English nominalized thematic structure. The English unmarked ideational/topical theme in (4.1a) carries given information which flows down in the following unmarked nominalized theme in (4.2a). Along with the constant information flow, the English unmarked nominalized theme is also a peripheral theme bearing new information. On the other hand, the translated unmarked ideational/topical theme in (4.1b) does not share its information with the following topical theme in (4.2b). Furthermore, the topical theme in (4.2b) is a misleading and ambiguous translation of the English nominalized theme in (4.2a) because it does not have thematic nominalization and exclusiveness. The English nominalized theme encloses an embedded clause who believed such stories which makes the nominal phrase those exclusive and this theme conveys the information that only those people who believe such stories are unworthy of the Lord’s table. Here, some specific believers have been mentioned. On the contrary, the translated Urdu clause in (4.2b) is not marked with nominalization rather it begins with a correlative marker ?o which correlates with the demonstrative vo in the following clause (4.3b). These clauses combined with correlatives do not involve thematic nominalization, so they cannot be recognized as a thematic equative. Consequently, the translated clauses in (4.2b) and (4.3b) give the information that the believers of such stories are unworthy of the Lord’s table. In other words, there remains a possibility that the non-believers of such stories or the believers of any other thing may also be unworthy of the Lord’s table. Such ambiguity is the outcome of the non-restrictive correlatives ?o-vo (which-that). However, another translation choice including restrictive embedded clause seems favorable to avoid misleading information e.g. vo log ?o ?n k?h?nijõ p?r j?kin r?kht?e he? ?q? ki mæz ke g?rd? bethne ke eh?l n?hi.
Conclusion
The conclusions have been drawn out by answering the research questions. First of all, to address the first question of this study, the possible patterns of nominalized themes in English and Urdu have been described. And after the description, it has been justified that both languages have their own specific grammatical realizations to create nominalized thematic structures. The formation of nominalized thematic structures varies due to the verbs marked with gender and numbers.
The second question has been addressed by analyzing the functional significance and thematic progression of nominalized themes in English and Urdu. It is obvious that both languages equally maintain functions of nominalized thematic structures until the unmotivated displacement of themes is not found. The English and Urdu nominalized themes go parallel in theme markedness but the difference is observed when the thematic information units become rhematic information units.
The last question has been addressed by screening the nominalized themes from the English and Urdu corpus. After screening, it is concluded that the author of the English text incorporates the nominalized themes to emphasize the most important and certain aspects of information. Likewise, the author of the Urdu text incorporates nominalized themes for the same purposes. It is also concluded that most of the English nominalized thematic structures have not been translated into Urdu properly. During translation, the translator has made unmotivated displacements of themes that are unable to preserve the information focus in the Urdu text. In the end, it is suggested that the translators should be careful about the parameters of nominalized thematic structures in Urdu. In this way, it will be possible to translate the English nominalized thematic structures with their full force and emphasis into Urdu.
References
- Achebe, C. (1958). Things fall apart. New York: Random House, Inc.
- Bhatt, R. (1997). Matching effects and the syntax-morphology interface: Evidence from Hindi correlatives. MIT Working Papers in Linguistics, 31. MIT Press.
- Butt, M., & King, T. H. (2007). Urdu in a parallel grammar development environment. Language Resources and Evaluation, 41(2), 191-207.
- Caffarel-Cayron, A., Martin, Jr, & Matthiessen, C. M. (2004). Language Typology: A Functional Perspective (Current Issues in Linguistic Theory) (First Edition). John Benjamins Publishing Company.
- Francis G. (1990). Occasional Papers in Systemic Linguistics, Theme in the daily press 4, 51-88.
- Halliday, M. A. K. (1967). Notes on transitivity and theme in English: Part 2. Journal of Linguistics, 3(2), 199-244.
- Halliday, M. A. K. (1985). An introduction to functional grammar. London: Edward Arnold.
- Halliday, M. A. K. (1994). An introduction to functional grammar. London: Edward Arnold.
- Halliday, M. A. K. & Martin, J. R. (1993). Writing science: literacy and discursive power. London: Falmer.
- Kim, M. (2007). A discourse based study on theme in Korean and textual meaning in translation. PhD thesis, Macquarie University, Sydney.
- Kim, M. (2007a). Using systemic functional text analysis for translator education: An illustration with a focus on the textual meaning. Interpreter and Translator Trainer, 1(2), 223-246.
- Kim, M. (2011a). A systemic functional approach to the tangled thread issues of Korean theme study. International Review of Korean Studies, 8(1), 101-137.
- Kim, M. (2011b). A study on target readers' reactions to different theme choices in English translations of a Korean short story. In Cho, E. (Ed.). Translation studies, what does it study: Linguistic, cultural and social approaches, 53-84. Seoul: Dongkuk University Press.
- Kunz, K., Teich, E., Hansen-Schirra, S., Neumann, S., & Daut, P. (2014). Caught in the middle - Language use and translation. Saarbrücken: Saarland University Press.
- O'Donnell, M. (2008). Demonstration of the UAM CorpusTool for text and image annotation. Proceedings of the ACL-08: HLT Demo Session (Companion Volume), 13-16. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Rose, D. (2001). The western desert code: An Australian cryptogrammar. The Australian National University. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
- Schmidt, R. L. (1999). Urdu: An Essential Grammar. London: Routledge
- Steiner, E. (2002). Grammatical metaphor in translation: Some methods for corpus- based investigations. In Hasselgård, H., Johansson, S., Behrens, B., & Fabricius- Hansen, C. (Eds.). Information structure in a cross-linguistic perspective, 213-228. Amsterdam: Rodopi.
- Ullah I. (1991). Bikharti Duniya. Lahore: Nigarshat Publications.
Cite this article
-
APA : Yaqub, H., Ahsan, A., & Iqbal, M. (2022). Metafunctional Analysis of Nominalized Thematic Structures in English and Urdu. Global Language Review, VII(I), 55-70. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2022(VII-I).06
-
CHICAGO : Yaqub, Humaira, Ansa Ahsan, and Mubashir Iqbal. 2022. "Metafunctional Analysis of Nominalized Thematic Structures in English and Urdu." Global Language Review, VII (I): 55-70 doi: 10.31703/glr.2022(VII-I).06
-
HARVARD : YAQUB, H., AHSAN, A. & IQBAL, M. 2022. Metafunctional Analysis of Nominalized Thematic Structures in English and Urdu. Global Language Review, VII, 55-70.
-
MHRA : Yaqub, Humaira, Ansa Ahsan, and Mubashir Iqbal. 2022. "Metafunctional Analysis of Nominalized Thematic Structures in English and Urdu." Global Language Review, VII: 55-70
-
MLA : Yaqub, Humaira, Ansa Ahsan, and Mubashir Iqbal. "Metafunctional Analysis of Nominalized Thematic Structures in English and Urdu." Global Language Review, VII.I (2022): 55-70 Print.
-
OXFORD : Yaqub, Humaira, Ahsan, Ansa, and Iqbal, Mubashir (2022), "Metafunctional Analysis of Nominalized Thematic Structures in English and Urdu", Global Language Review, VII (I), 55-70
-
TURABIAN : Yaqub, Humaira, Ansa Ahsan, and Mubashir Iqbal. "Metafunctional Analysis of Nominalized Thematic Structures in English and Urdu." Global Language Review VII, no. I (2022): 55-70. https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2022(VII-I).06