Abstract
The aim of the present study is to understand psychological discursiveness in the speech delivered by former Prime Minister of Pakistan Imran Khan on national issues. In this study, cognitive (schematic) and linguistic analysis are hybridized at lexical, syntactic and pragmatical levels to find out the results. The study is mixed in its nature and there have been utilized Atomistic Morphological Analysis Method, Syntactic Analysis (Jegede, 2020) and Cognitive Pragmatic Communication Theory (Sperber & Wilson, 2004). Frequent use of first-person pronouns, declarative sentences and other utterings denotes that the speaker is intended to keep the speech relevant to the aspects like power, hegemony and ideology. Furthermore, cognitive linguistic analysis reveals that the speaker is determined to present his agenda as positive ourselves and negative other-selves for the promotion of his own hegemonic agenda which is wrapped in the ideology.
Key Words
Morphological Analysis, Syntactic Analysis, Cognitive Pragmatic Communication, Imran Khan, Speech
Introduction
The study of languages, their structure, and how they manifest themselves is complex. Human brain processes and interpret information based on perception, communication style and content of language. The current study explores cognitive and linguistic components of speech on national issues. Imran Khan served as Pakistan’s prime minister from April 2018 to April 2022. His talks are heavily loaded with information about media freedom, corruption, and other examples to make his points clear. It is crucial to emphasize cognitive and linguistic characteristics in order to control the intended expectations in the speech. His speeches are usually focused on comparisons between Eastern and Western elements and the standard of justice.
Dramnescu (2016) comprehended distinctive features of several practical techniques to evaluate political discourse. Speech plays a major role in social, psychological and political aspects, hence studying the character of political speeches received the most attention. The results demonstrated that the "speaking act," which is based on the current activities, is a crucial pragmatic. Politicians utilise the "Speech Act" to persuade the public about the future, but it's vital to remember that the interpretation of the speech should be interpreted based on context because there is a significant connection between the context and text.
The basis for morphological analysis is the word selections, which may contain various word types, and word constituents in various forms. On the other side, the syntactic analysis reveals the sentence structure, word choice, and word placement in the text. Pragmatic analysis is the study of cultural meanings, and it frequently incorporates a cultural element along with discourse analysis.
The large discipline of morphological analysis examines the words and morphemes used in a text or speech. The abstractive framework and the atomistic framework are the two basic morphological analysis frameworks that Blevins (2020) has presented. In this study, an atomistic framework was used that generally addresses morphemic analysis.
The syntax is the term for the instrument that aids in understanding sentences and provides interpretations in contexts. Words are organized in different sentences to clarify the phrase structure and establish the syntactic analysis. Chomsky’s vast semantic-syntactic theory, however, demonstrates that a variety of meanings can be extrapolated. The dynamic syntactic theory can be used to analyse the various functions that can result from the movement of the elements.
According to Chomsky’s interpretation (1995), the cognitive domains are in charge of not only the transformation into new perception and retrieval but also the interpretation of the phrases.
Pragmatics is understanding aspects of actual circumstances. Fundamental components and connections between language, society, and culture are investigated. To appraise the things that exist in other cultures, one must have a thorough understanding of their values and language. It characterises the phenomenon of the situation as well as the components that are interpreted differently in society are values and language. The media, literature, sermons, and descriptions of products make it simple to understand the nation’s aims. Values reflect how a country views the world and its circumstances.
Ojukwu and Osuchukwu (2015) conducted a study to comprehend the felicity requirements and significance of speeches. Austin’s Speech Act Theory was used with Grice’s cooperative principles and Searle’s Taxonomy. It demonstrated that Nelson Mandela’s remarks were made up and adhered to J. L. Austin’s ideal conditions (1962). The lectures are based on the truth because Nelson Mandela kept his commitments, and Grice’s cooperative ideals are also applied in those addresses.
Wnagatia et al. (2016) researched to comprehend the approaches taken by Kenyan politicians when giving speeches. Sperber and Wilson (1985, 1995) and Wilson and Sperber (2004) were the study’s adopted methods for providing practical interpretations of the data. Kenya is enriched by the forty-two tribes that make up its distinct cultural population. The data was gathered through observation, and the speeches from the by-election in December 2013 served as the sample. The study’s conclusions demonstrated how Kenyan politicians exert influence over the public and present an elite ranking system. They are designed to manipulate people’s perceptions in order to exercise authority over them.
Jegede (2020) conducted a study to determine how syntactic techniques were used in Donald Trump’s inauguration speech. The study looked at the frequency of the devices using both qualitative and quantitative methodologies. The main emphasis was on comprehending how speech-making technologies worked. The study’s findings demonstrated that Donald Trump’s speech was compelling and that he used basic, compound, and complex sentences. The study also discovered that using syntactic devices helped speakers convey their intended intentions, create coherence in their speeches, and set expectations for Americans.
Sadia et al. (2020) identified the diplomatic techniques employed by Pakistani and American politicians on talk shows that incorporate elements of their own countries. The research methodology used was based on the politeness strategies model developed by Brown and Lavinsons in 1987. Five interviews with politicians from Pakistan and the United States made up the study’s sample. The study’s findings showed that Pakistani and American politicians employ politeness techniques in various ways. Their goal was to make their speeches convincing and illustrative.
Ahmad et al. (2020) analyzed a speech to UN General Assembly on 27th Sep 2019, Prime Minister Imran Khan identified certain verbal actions related to Islamophobia. This study looked at the categories, overlapping patterns, and directness or indirectness of Imran Khan’s speaking acts. The speech acts were looked at both qualitatively and quantitatively from each of these perspectives. This study’s analytical framework was the Speech Act theory, which Austin and Searle created. The findings revealed that he regularly speaks directly and performs as many representative and expressive behaviours as he can. The conclusion of the paper argues that the speech act analysis reveals the Pakistani Prime Minister’s factual, educational, and supporting nature.
Imran Khan, the current prime minister of Pakistan, gave a speech that will be examined in the current study from the perspective of SFL. This analysis will focus on the speech’s interpersonal meta-function according to the Hallidayan Model. Examining language’s role in communication is the aim of the study. This study examines the text of Imran Khan’s speech, which was given on February 10 at the World Government Summit in Dubai. To gather and analyze data from Imran Khan’s speech, the study used qualitative and quantitative research methods. When analyzing the propositional structure of Imran Khan’s speech, the researchers analyzed the Mood systems of the sentences. The speech is thus broken up into sentences (clause complexes), with each clause being interpersonally analyzed. The structural elements of a sentence, its choice of Declarative, Imperative, Interrogative, or forms, are controlled by the mood system. Declarative, interrogative, and imperative sentences all naturally express assertions, inquiries, and commands, respectively. This study explains the idea of mood in great detail and shows how readers need to have a firm grasp of language’s grammatical functions from classical grammar to modern grammar (Ashiq et al., 2021).
The current study will elaborate on the morphological components and their meanings used by the speaker, the usage of syntactic components for certain utterances, and the speaker’s orientation to meaning as it exists in society through cognitive pragmatic analysis. The objective of the study is to explore the cognitive and linguistic features of Imran Khan's speech on national issues in recent times.
Method
The current study used both qualitative and quantitative approaches. Imran Khan, a former prime minister, delivered a fifteen-minute speech about fighting corruption and promoting national development was taken as a sample of the study. The speech was downloaded then the fifteen-minute clip was translated into Urdu, the native language of the speaker. The discourse was also transcribed in English.
The text was split into its individual components as the next step, and it was then entered into an Excel sheet using the text splitter website. The romanization of Urdu terms was done for transcription purposes because the research demands that words be transitioned with a specified data gloss. The Romans were transcribable using a transcription website, but many words were missed, therefore the Urdu words had to be manually transcribable. The meanings of each word are then generated independently using the online Google translator at the following stage, and finally, the full phrases are translated using Google Translate. Due to the possibility of different meanings, the procedure of proofreading is used to determine the final format.
Morphological Analysis
Understanding the composition and formation of words, as well as their intended illustrations, is known as morphological analysis. According to Blevins (2020), the denotative examples of the morphemes serve as the foundation for the Atomistic framework. The components are referred to as the “building blocks” for more elaborate statements. According to this method of morphological analysis, the meanings associated with the minimal forms are placed in “entries” of lexical representation but are contained in very elucidated qualities of particular meanings in the grammar.
Syntactic Analysis
The conceptualization of comprehending the structure of sentences in the light of grammatical principles is known as syntactic analysis. The knowledge about the language’s employed structures, their forms for particular meaning orientation, and their contextual formation is provided by syntactic analysis. In order to comprehend the grammar, Chomsky (1995) addressed the phrasal structure. According to Jedege (2020), political language has many forms and patterns, which can be better comprehended by utilising its syntactic elements. The sentence structures, verb tenses, and usage of conjunctions, adverbs, and pronouns are some of these strategies. The best tool for understanding sentence structures, also known as syntactic analysis, is syntactic devices.
Cognitive-Pragmatic Communication (Pragmatic Analysis)
Sperber and Wilson (1986) proposed the cognitive-pragmatic communication theory known as relevance theory for the interpretation and understanding of written or spoken words. This strategy is referred to as the inferential strategy since the listener infers the meanings from the evidence presented. The theory, which is for the understanding of innate meanings, is also discussed in Sperber and Wilson (2004). This notion serves as a filter to draw out the meanings that are in the speaker’s mind.
According to Wangatiah et al. (2016), the relevance theory is applied to the following three steps of demonstration.
Context Notion: Context is known as the presumptions of a listener and it is referred to as a psychological construct created by the speaker and listener (Sperber &Wilson, 1995).
Fundamentals of Communication Relevance: Any act of ostensive communication conveys the presumption of optimal relevance (Sperber & Wilson, 2004, p. 612).
Process for Understanding Relevance Theory: Human cognition is designed to be in a state of optimising relevance (Sperber & Wilson, 2004).
The listener’s intentions for integrating the information represented by the utterances are known as cognitive effects. Building contextual implications, supporting preconceived notions, and contradicting and eradicating preconceived notions are all examples of positive cognitive consequences.
Findings and Discussion
Understanding the use of
morphemes, their structure, and their interpretations is known as morphological
analysis. These structures are depicted in atomistic frameworks as the “building
blocks” for the formation of words (Blevins, 2020). Although the discourse is
in Urdu, the language also has root word structures and affixes.
Imran Khan prefers to utilise the
singular forms of words. The word “society” (/mrae/) contains two allomorphs,
but due to its usage, it only has one meaning. The second is /mr/, which
indicates that words can be distinguished by their / sounds. Although it is
used as one for one as in /mrn/ (Societies), the usage of plural forms indicates
that the speaker is referring to two distinct societies while still examining
them independently, such as Pakistan and Britain. The plural form of the terms
is indicated by the letter /n/.
The plural versions of words are created
by using the sounds /en/ and /n/, and Imran Khan regularly employs this form in
his speech.
/ l??gu?n/ Although (: people) is the
plural form of (: people), both words share the same meanings as a result of
their usage.
/behr hl/(: Anyway) is
another term that is employed as an adverb in speech. I based the root terms on
several meanings. /behr hl/: (present or circumstance), but to prefix, it has
been changed from a noun to an adverb.
Syntactic Analysis
Understanding the grammatical foundations of
sentences is the process of syntactic analysis. Despite widespread recognition,
the Chomsky (1995)
model is only applicable to phrasal structures. Jegede (2020)’s
new dimensions demonstrate a more sophisticated understanding of patterns of
sentences.
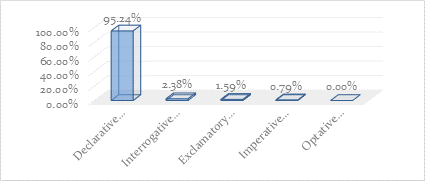
Types of Sentences (Functional)
Table 1
|
Sentence Type |
Declarative |
Integorrative |
Exclamatory |
Imperative |
Optative |
Total |
|
Frequency |
120 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
126 |
|
Percentage |
95.24% |
2.38% |
1.59% |
0.79% |
0.00% |
100.00% |
Graph 1
Analysis
The collected data indicate
that Imran Khan intends to employ declarative in 120 sentences to make his
speech sound more worrisome. Imran Khan utilises 95.24% of declarative phrases
in his speech, as shown by Table No. 1 and Graph No. 1. This makes the listener
more receptive and able to comprehend his discourse. Declarative sentences make
the meaning obvious, but other phrase kinds may rely on the speaker’s speech
process. According to data, using declarative sentences improves the clarity of
the speaker’s message delivery.
Types of Sentences
(Structural)
Table 2
|
Sentence Type |
Simple |
Compound |
Complex |
Total |
|
Frequency |
14 |
100 |
12 |
126 |
|
Percentage |
11.11% |
79.37% |
9.52% |
100.00% |
Graph 2
Analysis
Imran Khan regularly uses
compound sentences because his speech is dependent on the circumstances and the
context. This demonstrates Imran Khan’s intention to present information in a
factual and logical manner so that his message would be comprehended. 11.11% of
phrases are basic, 79.37% are compound, and 9.52% are complex, according to
Table No. 2 and Graph No. 2. The speech is intended to be more exact and
straightforward for understanding and semantics because using complex sentences
could make it complex.
Use of Pronoun
Table 3
|
Pronouns |
Ist Person |
2nd Person |
3rd Person |
Total |
||||
|
???? ????? ???? |
??? ???? |
??? ??? |
??? ???? ?? ?? |
??? ???? ?? ?? |
??? ?????? ?? ?? |
??? ?? |
||
|
I |
We |
You |
He |
She |
They |
It |
||
|
Frequency |
47 |
19 |
14 |
26 |
1 |
15 |
18 |
140 |
|
Percentage |
33.57% |
13.57% |
10.00% |
18.57% |
0.71% |
10.71% |
12.86% |
100.00% |
Graph 3
Analysis
Since the speech is on a
state issue, Imran Khan, a former prime minister, is well-versed in matters of
state and frequently uses the first person. The data in Table No. 3 and Graph
No. 3 demonstrates that “I” is commonly utilized accounting for 33.57 percent
of all pronoun usage. The percentages for the use of We, You, He, She, Them and
It are correspondingly 13.57, 10.00, 18.57,0.71, 10.71, 12.86 per cent. So it
is indicated by the pieces of evidence that person illustrations are regularly
and logically offered by the speech of Imran Khan.
Use of Conjunctions
Table 4
|
Conjunctions |
?????? |
?? ??? |
??? |
???? |
?? |
?? |
??? |
|
|
Because |
Therefore |
and |
but |
then |
that |
If |
Total |
|
|
Frequency |
5 |
6 |
37 |
12 |
19 |
21 |
12 |
112 |
|
Percentage |
4.46% |
5.36% |
33.04% |
10.71% |
16.96% |
18.75% |
10.71% |
100.00% |
Graph 4
Analysis
Because speech uses compound
sentences the majority of the time, the word “and” is used 33, 04% of the time.
Other conditions are employed as well, but the conjunctions “and” and “that,”
which are commonly used, indicate that the speaker wants to utilise compound
sentences more often in the predetermined concept that the message can be made
more obvious and illuminated.
Use of Modality
Table 5
|
Modality |
?? ??? |
?? |
?????? |
|
|
Can,
could |
Will,
Shall |
Must |
Total |
|
|
Frequency |
8 |
9 |
6 |
23 |
|
Percentage |
34.78 |
39.13 |
26.09 |
100 |
Graph 5
Analysis
Most often, modal verbs are
utilised in relation to strength and examples. The speaker’s usage of “will,
shall” and “can, could” demonstrates that the desired powers for system
orientation, which is the major subject of power, are beyond the senses. Since
these examples are absent from the speech, it can be claimed that the speech is
more declarative.
Pragmatic Analysis Using Cognitive Pragmatic
Communication Theory
Table
6
|
Normal
Font Data |
IPA
Transcription |
Data
Gloss |
Data
Transcription |
|
?? ? ??? ?? ?? ??? ? ???? ???? ???? ?? ?? |
n?ins?fi |
Injustice
|
Raising
your voice in front of injustice |
|
Kei |
Of the
|
||
|
s?m?? |
In
front |
||
|
?pn?? |
Your |
||
|
??w??z |
the
voice |
||
|
b?l?nd |
To
Raise |
||
|
k?rn? |
Analysis
The intentions of the
speakers are clear from the above-mentioned line of utterances, which is
advocating freedom within the context of duty, with that responsibility being
the “eradication of corruption.” According to the relevance theory model that
has been established, the speaker intends to communicate the features of
corruption so that the contextual and relevant element may be seen in his
speech, which in turn leads to the principle of relevance. The process of the
listener’s perception is the last phase in comprehension theory analysis (Sperber
& Wilson, 2004). The speaker’s intention is
to “understand the responsibility due to freedom” and “country building is
important because of freedom,” which the listener might infer from the current
phrases.
Table
7
|
Normal
Font Data |
IPA
Transcription |
Data
Gloss |
Data
Transcription |
|
??? ? ???? ??? ??? ???? ?? ???? |
/gh?l?m |
Slave |
Slaves
can never do great things. |
|
k?bh?i: |
Ever |
||
|
b?r? |
Big |
||
|
k??m |
The
Work |
||
|
n?hi:n |
Never |
||
|
k?: |
Do |
||
|
s?tkei/ |
Can |
Analysis
Wodak (2012) has said that the general meaning of power over discourse
is called access to the public and it is made possible by the conventional
language game where the actors find themselves. Similarly, Ex-Prime Minister
Imran Khan is determined to exercise the power over discourse by saying ??? ? ????
??? ??? ???? ?? ????, is
trying to access the public by the language game. Furthermore, Ex-Prime
Minister Imran Khan is either giving suggestions to the nation or advising his
political workers for sustaining the power. Van Dijk (1989a) has explained that
communication, discourse, interactions and actions are measured by social
cognition and he tries to monitor the corruption by using these strategies that
is presumed by the listeners and audiences since the day of independence. There
is a determination of the speaker in the statement to produce ourselves as a
positive and ourselves as a negative. So the listeners can also be manipulated
ideologically by incitement of their emotions regarding corruption (Sperber
&Wilson, 2004). Van Dijk (1993, p.254) has elaborated that power is linked to the control
of one group over the other group and such controls are pertaining to cognition
and action which influence the minds. The mind's influence is also linked with
one's own interest so there might be a chance that Mr. Khan may be looking for
the influence of the masses' mind by the use of these. He (1993, p.254-55) says
that although power relations are subtle and complex yet there is a chance of
power abuse as well.
Table
8
|
Normal
Font Data |
IPA
Transcription |
Data
Gloss |
Data
Transcription |
|
?? ?? ?? ??? ?? ??? ?? ???? ?? ???
????? ? ???- |
s?b |
All |
For
two to three hundred years all the scientists were Muslims. |
|
d?: |
Two |
||
|
ti:n |
Three |
||
|
s?? |
Hundred |
||
|
s??l |
Years |
||
|
t?k |
For |
||
|
s?r? |
All |
||
|
s?i?ntist |
Scientist |
||
|
m?s?lm?n |
Muslims |
||
|
?? |
Were |
Analysis
The historical incident’s
motivation has been a fantastic instrument for interpretation. The speaker was
trying to convey to the listeners that “they had a fantastic history” and that
the current authorities are favoured making the nation superb. There is again
the propagation of positive oneself and negative other-self in order to present
the cognitive control as Van Dijk (1993, p.257) has explained that
social cognition is social because they are shared by the group members or
society as a whole. According to the relevance theory (Sperber & Wilson, 1985, 1996; Sperber & Wilson, 2004), the listener is expected
to have relevance with the excellent history, and the speaker’s idealised
vision is clearly expressed in the first sentence.
Speech
Extract
“I
remember Farooq Leghari when he came to the government in 1996, he gave me the
entire file that Baynazeer and Zardari had withdrawn one and a half billion
dollars from the country. Now I am talking about Chatnawa and Nawaz Shareef has
also taken one and a half billion dollars out of the country, so I was against
corruption in politics”.
Analysis
The speaker appears to have
sought to use such a scenario to relate the history with the current situation
and make the listener relevant to the past. The listener would comprehend that
the circumstances at hand are a result of earlier occurrences. The listener’s
cognitive effects are what matter
most in terms of relevance
(Sperber & Wilson, 2004), which is why lines are interpreted
as expressing “hatred” against the opponents and what would be implied from the
speaker’s point of view. The speaker can be understood as attempting to alter
the listener’s mood and making an appeal to put the current situation in a
historical context.
“And corruption is one of
the symptoms of a country where there is no rule of law, where there is no rule
of law, there is also corruption.”
Analysis
According to Sperber and
Wilson (2004), the listener’s realm of knowledge
determines how relevant a message is to them. The manner in which the words
were spoken indicates that the speaker intended for the listener to understand
that the hater would assume that there is a connection between corruption and
the rule of law. A crooked individual simply thinks about how limited time and
resources are, not how to understand them. The speaker is asked to understand
that rule of law violations depend on corruption and that rule of law voices
would rise as a result.
Conclusion
It might be inferred that the speaker wants to persuade the audience to support a particular attempt or behaviour by presenting state themes and issues to them. There is another chance that he might be determined to control the mind of the masses through social cognition and dominance for the maintenance and resistance of his own ideology. According to morphological research, the singular forms are prevalent and the speaker uses borrowing as a code-switching technique. According to syntactic analysis, the speaker intends to depict characteristics and tendencies favourably while advising listeners to be worried about the state’s problems. According to the results of the cognitive pragmatic communication analysis, the speaker wants to have an impact on how people think and get them to act in ways of anti-corruption and supportive of the rule of law.
References
- Ahmed, H. R., Amir, S., & Ahmad, F. (2021). A Speech Act Analysis of the Prime Minister of Pakistan Imran Khan’s Speech at Unga with Respect to Islamophobia. International Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 5(2), 59–71.
- Ashiq, N., Bi, N. B., Shahid, M. A., & Shaffaqat, M. (2021). Interpersonal Analysis of Imran Khan's Speech: A Study Based on SFG. American Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences Research (AJHSSR), 5(6), 308-314.
- Blevins, P. J. (2020). Tow Frameworks of Morphological Analysis. Research Gate.
- Chomsky, N. (1995). The Minimalist Program. (Current studies in linguistics 28.) Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Drămnescu, B. (2016). Pragmatic Approaches in the Analysis of the Political Discourse. Trivent Publishing.
- Jegede, O. O. (2020). Syntactic Analysis of Donald Trump’s Inaugural Speech. ELS Journal on Interdisciplinary Studies in Humanities, 3(3), 317–327.
- Khan, I. (2022). Imran Khan’s Key Notes.
- Ojukwu, K. C. & Osuchukwu, N.A. (2019). A Pragmatic Analysis of Selected Political Speeches of Nelson Mandela. Journal of the English Scholars’ Association of Nigeria, 21(2), 1-34
- Sadia, S. P., Asghar, M. & Asghar, T. D. (2020). A Pragmatic Analysis of Politeness Strategies Used By Pakistani and American Politicians in Interviews. Ilkogretim Online - Elementary Education Online, 19 (4), 3774-3783.
- Sperber, D. & Wilson, D. (2004). “Relevance Theoryâ€. In Horn, L. & Ward, G. (Eds.). The Handbook of Pragmatics. p.p. 633- 657. Oxford: Blackwell.
- Sperber, D., & Wilson, D. (1986). Relevance: Communication and cognition. Oxford: Basil. Blackwall.
- Sperber, D., & Wilson, D. (1995). Postface to the second edition of Relevance: Communication and Cognition. Blackwell: Oxford
- Van Dijk, T. A. (1993). Principles of Critical Discourse Analysis. Discourse & Society, 4(2), 249–283.
- Van Dijk, T.A. (1989). `Social Cognition and Discourse', in H. Giles and R.P. Robinson (eds) Handbook of Social Psychology and Language, pp. 163-183. Chichester: Wiley.
- Wangatiah, I. R., Ongarora, D., & Matu, P. (2016). Political Speeches and National Integration: A Pragmatic Analysis of selected Political Speeches in Kenya. Multilingual Academic Journal of Education and Social Sciences, 4(1), 57– 70.
- Wodak, R. (2011). Language, power and identity. Language Teaching, 45(2), 215– 233.
Cite this article
-
APA : Ramzan, M., Javaid, Z. K., & Khan, M. A. (2023). Psychological Discursiveness in Language Use of Imran Khan's Speech on National Issues. Global Language Review, VIII(II), 214-225 . https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2023(VIII-II).19
-
CHICAGO : Ramzan, Muhammad, Zartashia Kynat Javaid, and Misbah Afsheen Khan. 2023. "Psychological Discursiveness in Language Use of Imran Khan's Speech on National Issues." Global Language Review, VIII (II): 214-225 doi: 10.31703/glr.2023(VIII-II).19
-
HARVARD : RAMZAN, M., JAVAID, Z. K. & KHAN, M. A. 2023. Psychological Discursiveness in Language Use of Imran Khan's Speech on National Issues. Global Language Review, VIII, 214-225 .
-
MHRA : Ramzan, Muhammad, Zartashia Kynat Javaid, and Misbah Afsheen Khan. 2023. "Psychological Discursiveness in Language Use of Imran Khan's Speech on National Issues." Global Language Review, VIII: 214-225
-
MLA : Ramzan, Muhammad, Zartashia Kynat Javaid, and Misbah Afsheen Khan. "Psychological Discursiveness in Language Use of Imran Khan's Speech on National Issues." Global Language Review, VIII.II (2023): 214-225 Print.
-
OXFORD : Ramzan, Muhammad, Javaid, Zartashia Kynat, and Khan, Misbah Afsheen (2023), "Psychological Discursiveness in Language Use of Imran Khan's Speech on National Issues", Global Language Review, VIII (II), 214-225
-
TURABIAN : Ramzan, Muhammad, Zartashia Kynat Javaid, and Misbah Afsheen Khan. "Psychological Discursiveness in Language Use of Imran Khan's Speech on National Issues." Global Language Review VIII, no. II (2023): 214-225 . https://doi.org/10.31703/glr.2023(VIII-II).19